Introduction
Urban planning is experiencing a transformative shift due to Geographic Information Systems (GIS). As cities evolve into smarter, more efficient spaces, GIS becomes a cornerstone in the decision-making process for sustainable urban infrastructure and development. In this article, we’ll explore how GIS is crucial to urban planning, its role in smart city projects, and how it enhances environmental resilience and community involvement.

GIS and Urban Planning: The Basics
GIS enables planners to visualize, analyze, and interpret spatial data. This system gives city planners a comprehensive, real-time overview of various urban elements like land use, population density, transportation networks, and environmental factors. Unlike traditional methods relying on static data, GIS integrates real-time updates from multiple sources, allowing for dynamic decision-making that improves city layouts and infrastructure.

By mapping geographical features, urban planners can make informed decisions that balance city growth with environmental sustainability. Land-use optimization, transportation planning, and infrastructure upgrades are significantly enhanced through GIS’s data-driven approach.
Optimizing Land Use and Zoning
One of GIS’s core applications in urban planning is managing land-use and zoning. With rapid urbanization, effective space management is vital. GIS helps planners evaluate current land use, predict future demands, and balance competing interests, such as residential areas, industrial zones, and green spaces.

GIS can simulate various zoning scenarios, allowing planners to visualize outcomes before implementing changes. For example, GIS enables planners to analyze the impacts of commercial expansion in residential neighborhoods, helping prevent overdevelopment and ensuring sustainable growth. Furthermore, historical data can be overlaid with current environmental conditions, aiding in making long-term zoning decisions that balance development with natural resource preservation.
Smart City Development
Smart cities are becoming the epitome of urban innovation, and GIS lies at the heart of this revolution. In smart cities, real-time data from IoT devices, sensors, and surveillance systems is integrated into GIS platforms, allowing city planners to make decisions based on accurate, live data.
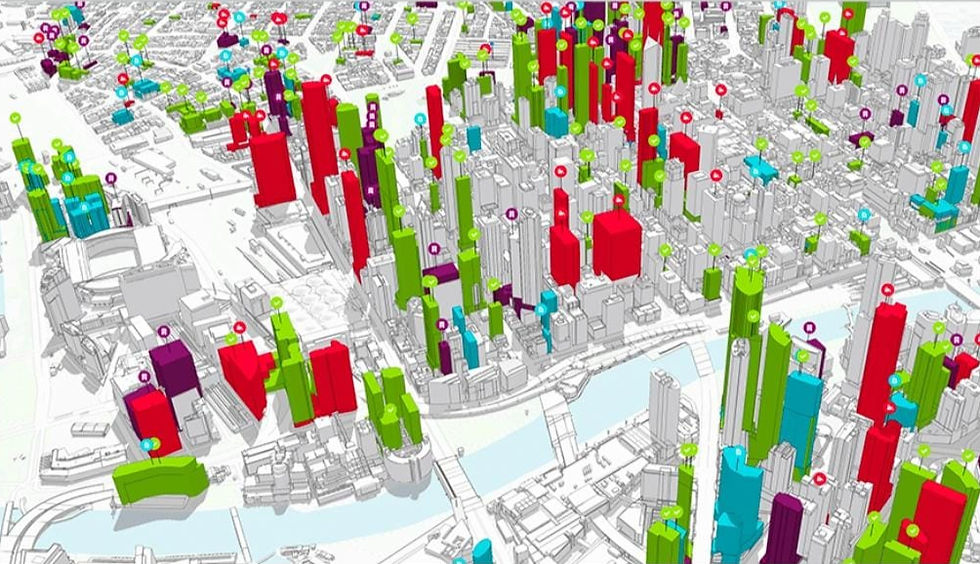
Cities like Singapore have successfully used GIS for smart city initiatives. Singapore leverages GIS to manage traffic systems, optimize public services, and ensure that resources like energy and water are used efficiently. The real-time spatial analysis provided by GIS helps smart cities achieve sustainability goals, improve public safety, and enhance overall quality of life.
Improving Infrastructure and Resource Management
GIS significantly impacts urban infrastructure planning. Whether it’s designing new transportation networks, laying out utility lines, or building sewage systems, GIS provides the tools to simulate and model complex interactions between these systems. By visualizing how infrastructure elements interact with the environment, city planners can identify bottlenecks and weak points, ensuring better long-term planning.

GIS is also vital for managing resources and predicting future urban needs. For instance, GIS tools can forecast population growth and its effects on water supply, helping cities plan new pipelines or reservoirs in advance. GIS also aids in optimizing energy distribution, ensuring that power grids are prepared for future demands while minimizing their environmental impact.
Environmental Sustainability and Climate Resilience
In today’s climate-conscious world, cities must be built with sustainability in mind, and GIS is instrumental in achieving this. Urban planners use GIS to analyze environmental factors like flood zones, heat islands, and pollution levels, ensuring that new developments don’t exacerbate environmental issues.
GIS has been employed in coastal cities to map out flood-prone areas and develop strategies to protect communities. By simulating the impacts of sea-level rise, planners can decide where to implement barriers or raise buildings. In addition, GIS helps cities plan green infrastructure like parks and rain gardens that improve air quality and reduce the urban heat island effect.

GIS is essential for creating climate-resilient cities. It helps planners mitigate disaster risks by identifying vulnerable areas and developing evacuation routes and emergency response systems. This foresight ensures that urban spaces are better equipped to withstand natural disasters and changing climate patterns.
Public Engagement and Transparency
Modern urban planning emphasizes citizen participation, and GIS is a powerful tool for encouraging public involvement. Many cities now use web-based GIS platforms to share zoning maps, construction plans, and environmental reports with the public. Citizens can access these tools to provide feedback, ensuring that urban development aligns with their needs and preferences.

Public engagement through GIS is highlighted as a key factor in creating inclusive, equitable cities. For example, planners can invite citizens to suggest where new parks should be located or vote on public transportation routes. By involving the community in these decisions, cities can foster trust and ensure that development projects serve the entire population.
Conclusion
GIS is revolutionizing urban planning by providing tools for visualizing, analyzing, and modeling the intricate systems that make cities function. From optimizing land use to enhancing infrastructure and building climate resilience, GIS is indispensable in the creation of smarter, more sustainable cities. As urban areas continue to expand and face new challenges, the integration of GIS will become even more vital in shaping the future of urban development.

.png)
Comments